무엇을 찾고 계신가요?
무엇을 찾고 계신가요?
Are You Choosing the Right Thermistor?
May 20, 2025Whether designing a next-gen power supply, building an automotive BMS, or upgrading a smart appliance, selecting the right thermistor is more complex than it seems. This Q&A addresses some of the most common and technical questions engineers ask when working with NTC thermistors.
Q1: What’s the practical difference between B-value and Beta constant accuracy?
A: The B-value defines an NTC thermistor's exponential relationship between resistance and temperature. While a typical datasheet might state a nominal B25/50 value, real-world accuracy depends on tolerance, often ±1% to ±5%. A tighter Beta tolerance ensures better matching across thermistors and more reliable temperature readings, especially in analog circuits without software correction.
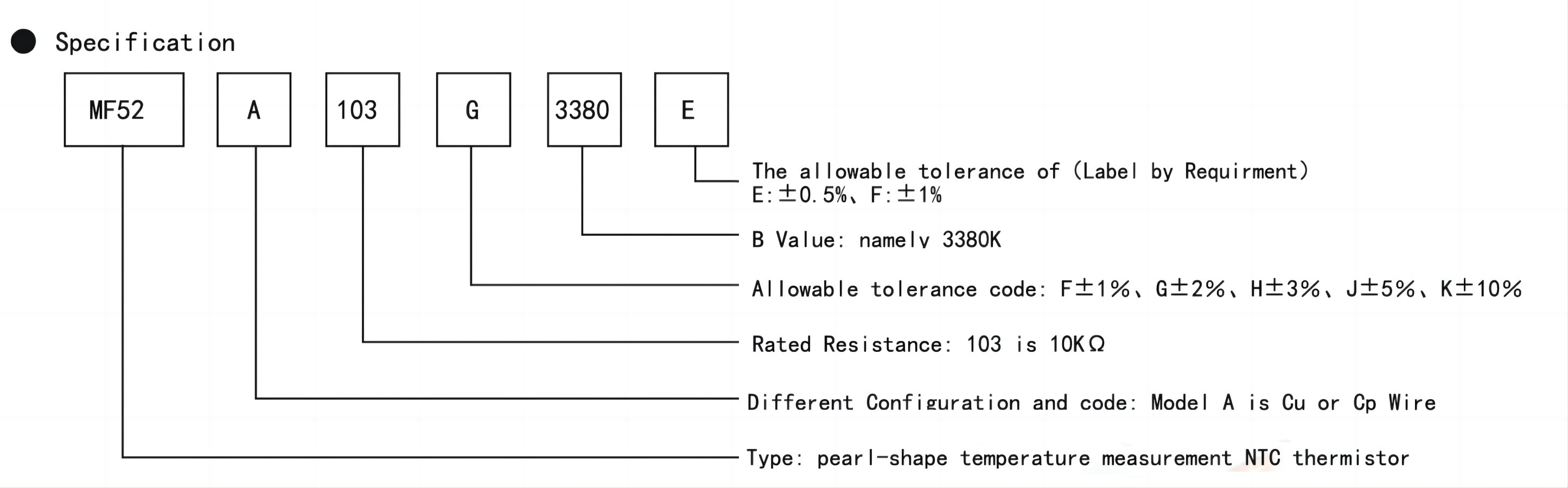
Q2: How does thermal time constant affect system response, and how is it measured?
A: The thermal time constant (τ) indicates how quickly a thermistor reacts to a step change in ambient temperature. Defined as the time needed to reach 63.2% of the total temperature change, a lower τ means faster reaction. It’s critical for applications like over-temperature protection in batteries or CPUs, where milliseconds count.
Q3: What causes self-heating in NTC thermistors, and how can it be mitigated?
A: Self-heating occurs when the thermistor’s own sensing current generates enough power to raise its temperature, skewing readings. To mitigate this, use low measurement currents (often <10 µA for high-resistance types) or select thermistors with higher dissipation constants (measured in mW/°C). Alternatively, use pulsed measurement techniques in precision systems.
Q4: How important is interchangeability between thermistors of the same part number?
A: Extremely important, especially in mass production. Good interchangeability ensures consistent R-T curves between batches. At Nanjing Shiheng, our automated manufacturing and strict SPC (Statistical Process Control) allow us to maintain tight R25 tolerances and B-value consistency, reducing calibration efforts on the customer side.
Q5: What are the key differences between epoxy-coated and glass-encapsulated thermistors in real-world use?
A: Epoxy-coated thermistors (e.g., MF52 series) are more economical and offer sufficient protection for moderate conditions. Glass-encapsulated types (e.g., MF58 series) provide higher reliability in environments with moisture, solvents, or high thermal cycling. Choose based on application stress level and expected product lifespan.
Q6: Can NTC thermistors be used in automotive environments, and what qualifications are needed?
A: Yes — but they must meet automotive-grade standards such as AEC-Q200. This includes testing for thermal shock, high humidity, mechanical vibration, and electrical overload. Our MF51, MF52, MF58, and MF59 series have passed AEC-Q200, making them suitable for EV battery packs, onboard chargers, and climate systems.
Thermistors are deceptively simple components, but selecting the right one — and using it correctly — requires attention to materials, tolerances, and circuit conditions. At Shiheng Electronic, we help engineers around the world navigate these details with expert advice, fast sampling, and high-reliability products.
Still have questions? Contact our team to discuss your project or request samples today.